Kashmir
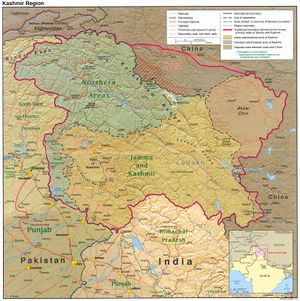

Kashmir (Kashmiri: کٔشِیر, कॅशीर; Dogri: कश्मीर; Ladakhi: ཀཤམིར; Balti: کشمیر; Gojri: کشمیر; Poonchi/Chibhali: کشمیر; Shina: کشمیر; Uyghur: كەشمىر) is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range. Contemporarily, Kashmir denotes a larger area that includes the Indian administered state of Jammu and Kashmir (Jammu, Kashmir, and Ladakh), the Pakistani administered Gilgit-Baltistan and Azad Kashmir, and the Chinese-administered regions of Aksai Chin and the Trans-Karakoram Tract. The United Nations[1] and other local entities use the designation Jammu and Kashmir to geographically denote said area.
According to the Mahabharata,[2] the Kambojas ruled Kashmir during the epic period with a Republican system of government [3][4][5] In the first half of the first millennium, the Kashmir region became an important center of Hinduism and later of Buddhism; later still, in the ninth century, Kashmir Shaivism arose.[6] In 1349, Shah Mir became the first Muslim ruler of Kashmir and inaugurated the Salatin-i-Kashmir or Swati dynasty.[7] For the next five centuries, Muslim monarchs ruled Kashmir, including the Mughals, who ruled from 1526 until 1751, then the Afghan Durrani Empire that ruled from 1747 until 1820.[7] That year, the Sikhs under Ranjit Singh, annexed Kashmir.[7] In 1846, upon the purchase of the region from the British under the Treaty of Amritsar, the Dogras—under Gulab Singh—became the new rulers. Dogra Rule, under the paramountcy (or tutelage) of the British Crown, lasted until 1947, when the former princely state signed an accession treaty with India after raiders from Pakistan attacked it. India applied to the United Nations a for resolution of the issue and a temporary line of control was created. Thus began a problem that still remains unresolved with the disputed territory now administered by the three countries of India, Pakistan, and the People's Republic of China.
Contents |
Etymology
The Nilamata Purana describes the Valley’s origin from the waters; का Ka (“water”) + शिमिरि Shimir (“to desiccate”), hence, Kaashmir denotes “a land desiccated from water”. An alternate nominal origin theory proposes that Kaashmir is a contraction of either Kashyap-mira or Kashyapmir or Kashyapmeru, denoting the “sea of Kashyapa” and the “mountain of Kashyapa”, eponyms of Kashyapa, the sage credited with having drained the primordial Satisar lake that occupied the Kaashmir valley before he reclaimed it from the water. Considering the Valley an embodiment of the goddess Uma, the Nilamata Purana gives it the place-name Kaashmira, from which derives the contemporary Kashmir place-name. Nonetheless, the Kaashmiris colloquially use the place-name Kashir, which is phonetically derived from Kaashmir, as noted in the Aurel Stein introduction to the Rajatarangini metrical chronicle.
In the Rajatarangini, a history of Kashmir written by Kalhana in the 12th century, it is stated that the valley of Kaashmir was formerly a lake. This was drained by the great rishi or sage, Kashyapa, son of Marichi, son of Brahma, by cutting the gap in the hills at Baramulla (Varaha-mula). Cashmere is a variant spelling of Kaashmir.[8]
History
Buddhism and Hinduism in Kashmir

The Buddhist Mauryan emperor Ashoka is often credited with having founded the old capital of Kashmir, Shrinagari, now ruins on the outskirts of modern Srinagar. Kashmir was long to be a stronghold of Buddhism.[9]
As a Buddhist seat of learning, it is possible that the Sarvāstivādan school dominated Kashmir.[10] East and Central Asian Buddhist monks are recorded as having visited the kingdom. In the late 4th century AD, the famous Kuchanese monk Kumārajīva, born to an Indian noble family, studied Dīrghāgama and Madhyāgama in Kashmir under Bandhudatta. He later became a prolific translator who helped take Buddhism to China. His mother Jīva is thought to have retired to Kashmir. Vimalākṣa, a Sarvāstivādan Buddhist monk, travelled from Kashmir to Kucha and there instructed Kumārajīva in the Vinayapiṭaka.
Adi Shankara visited the pre-existing Sarvajñapīṭha (Sharada Peeth) in Kashmir in late 8th century CE or early 9th Century CE. The Madhaviya Shankaravijayam states this temple had four doors for scholars from the four cardinal directions. The southern door (representing South India) had never been opened, indicating that no scholar from South India had entered the Sarvajna Pitha. Adi Shankara opened the southern door by defeating in debate all the scholars there in all the various scholastic disciplines such as Mimamsa, Vedanta and other branches of Hindu philosophy; he ascended the throne of Transcendent wisdom of that temple.[11]
Abhinavagupta (approx. 950 - 1020 AD[12][13]) was one of India's greatest philosophers, mystics and aestheticians. He was also considered an important musician, poet, dramatist, exeget, theologian, and logician[14][15] - a polymathic personality who exercised strong influences on Indian culture.[16][17]
He was born in the Valley of Kashmir[18] in a family of scholars and mystics and studied all the schools of philosophy and art of his time under the guidance of as many as fifteen (or more) teachers and gurus.[19] In his long life he completed over 35 works, the largest and most famous of which is Tantrāloka, an encyclopedic treatise on all the philosophical and practical aspects of Trika and Kaula (known today as Kashmir Shaivism). Another one of his very important contributions was in the field of philosophy of aesthetics with his famous Abhinavabhāratī commentary of Nāṭyaśāstra of Bharata Muni.[20]
Muslim rule
The Muslims and Hindus of Kashmir lived in relative harmony, since the Sufi-Islamic way of life that Muslims followed in Kashmir complemented the Rishi tradition of Kashmiri Pandits. This led to a syncretic culture where Hindus and Muslims revered the same local saints and prayed at the same shrines . Famous sufi saint Bulbul Shah was able to convert Rinchan Shah who was then prince of Kashgar Ladakh to an Islamic lifestyle, thus founding the Sufiana composite culture. Under this rule, Muslim, Hindu and Buddhist Kashmiris generally co-existed peacefully. Over time, however, the Sufiana governance gave way to outright Muslim monarchs[21] due to eternal Islamic policies as per 'Holy' Quran.[22][23]
First Muslim Ruler, Shah Mir Swati
In the beginning of 14th century a ferocious Mongol, Dulucha, invaded the valley through its northern side Zojila Pass, with an army of 60,000 men. Like Taimur in the Punjab and Delhi, Dulucha carried sword and fire, destroyed towns and villages and slaughtered thousands. His savage attack practically ended the Hindu rule in Kashmir. Raja Sahadev was the ruler then. It was during his reign that three men, Shah Mir from Swat (tribal) territory on the borders of Afghanistan, Rinchin from Ladhak, and Lankar Chak from Dard territory near Gilgit came to Kashmir, and played a notable role in subsequentive political history of the valley. All the three men were granted Jagirs by the King. Rinchin for 3 years became the ruler of Kashmir.
After the King, Shams-ud-Din Shah Mir Swati was the first Muslim ruler of Kashmir and the founder of the Shah Miri dynasty named after him. Jonaraja, in his Rajatarangini mentioned him as Sahamera. He came from Swat, the then (Tribal) territory on the borders of Afghanistan and played a notable role in subsequentive political history of the valley. Shahmir became the ruler of Kashmir and reigned for three years.He was the first ruler of Swati dynasty, which had established in 1339. Shah Mir was succeeded by his eldest son Jamshid, but he was deposed by his brother Ali Sher probably within few months, who ascended the throne under the name of Alauddin[1]
Some Kashmiri rulers, such as Sultan Zain-ul-Abidin who was popularly known as Baadshah (the King) (r.1423-1474), were tolerant of all religions in a manner comparable to Akbar. However, several Muslim rulers of Kashmir were intolerant of other religions. Sultãn Sikandar Butshikan of Kashmir (AD 1389-1413) is often considered the worst of these. Historians have recorded many of his atrocities. The Tarikh-i-Firishta records that Sikandar persecuted the Hindus and issued orders proscribing the residence of any other than Muslims in Kashmir. He also ordered the breaking of all "golden and silver images". The Tarikh-i-Firishta further states: "Many of the Brahmins, rather than abandon their religion or their country, poisoned themselves; some emigrated from their native homes, while a few escaped. After the emigration of the Brahmins, Sikandar ordered all the temples in Kashmir to be thrown down. Having broken all the images in Kashmir, (Sikandar) acquired the title of ‘Destroyer of Idols’."[24]
The metrical chronicle of the kings of Kashmir, called Rajatarangini, has been pronounced by Professor H.H.Wilson to be the only Sanskrit composition yet discovered to which the appellation "history" can with any propriety be applied. It first became known to the Muslims when, on Akbar's invasion of Kashmir in 1588, a copy was presented to the emperor. A translation into Persian was made at his order. A summary of its contents, taken from this Persian translation, is given by Abul Fazl in the Ain-i-Akbari. The Rajatarangini was written by Kalhana about the middle of the 12th century. His work, in six books, makes use of earlier writings that are now lost.
The Rajatarangini is the first of a series of four histories that record the annals of Kashmir. Commencing with a rendition of traditional history of very early times, the Rajatarangini comes down to the reign of Sangrama Deva, (c.1006 AD). The second work, by Jonaraja, continues the history from where Kalhana left off, and, entering the Muslim period, gives an account of the reigns down to that of Zain-ul-ab-ad-din, 1412. P. Srivara carried on the record to the accession of Fah Shah in 1486. The fourth work, called Rajavalipataka, by Prajnia Bhatta, completes the history to the time of the incorporation of Kashmir in the dominions of the Mogul emperor Akbar, 1588.
Sikh rule and Princely State
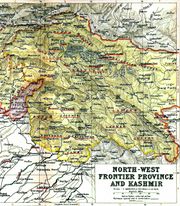
By the early 19th century, the Kashmir valley had passed from the control of the Durrani Empire of Afghanistan, and four centuries of Muslim rule under the Mughals and the Afghans, to the conquering Sikh armies. Earlier, in 1780, after the death of Ranjit Deo, the Raja of Jammu, the kingdom of Jammu (to the south of the Kashmir valley) was captured by the Sikhs under Ranjit Singh of Lahore and afterwards, until 1846, became a tributary to the Sikh power.[25] Ranjit Deo's grandnephew, Gulab Singh, subsequently sought service at the court of Ranjit Singh, distinguished himself in later campaigns, especially the annexation of the Kashmir valley by the Sikhs army in 1819, and, for his services, was appointed governor of Jammu in 1820. With the help of his officer, Zorawar Singh, Gulab Singh soon captured Ladakh and Baltistan, regions to the east and north-east of Jammu.[25]
In 1845, the First Anglo-Sikh War broke out, and Gulab Singh "contrived to hold himself aloof till the battle of Sobraon (1846), when he appeared as a useful mediator and the trusted advisor of Sir Henry Lawrence. Two treaties were concluded, of which the first gave the State of Lahore (i.e. West Punjab) to the British, whereas the second gave all the hilly or mountainous country situated to the east of Indus and west of Ravi" (i.e. the Vale of Kashmir) to Gulab Singh.[25][26] Soon after Gulab Singh's death in 1857, his son, Ranbir Singh, added the emirates of Hunza, Gilgit and Nagar to the kingdom.
The Princely State of Kashmir and Jammu (as it was then called) was constituted between 1820 and 1858 and was "somewhat artificial in composition and it did not develop a fully coherent identity, partly as a result of its disparate origins and partly as a result of the autocratic rule which it experienced on the fringes of Empire."[28] It combined disparate regions, religions, and ethnicities: to the east, Ladakh was ethnically and culturally Tibetan and its inhabitants practised Buddhism; to the south, Jammu had a mixed population of Hindus, Muslims and Sikhs; in the heavily populated central Kashmir valley, the population was overwhelmingly Sunni Muslim, however, there was also a small but influential Hindu minority, the Kashmiri brahmins or pandits; to the northeast, sparsely populated Baltistan had a population ethnically related to Ladakh, but which practised Shi'a Islam; to the north, also sparsely populated, Gilgit Agency, was an area of diverse, mostly Shi'a groups; and, to the west, Punch was Muslim, but of different ethnicity than the Kashmir valley.[28] After the Indian Rebellion of 1857, in which Kashmir sided with the British, and the subsequent assumption of direct rule by Great Britain, the princely state of Kashmir came under the suzerainty of the British Crown.
Year 1947 and 1948

Ranbir Singh's grandson Hari Singh, who had ascended the throne of Kashmir in 1925, was the reigning monarch in 1947 at the conclusion of British rule of the subcontinent and the subsequent partition of the British Indian Empire into the newly independent Union of India and the Dominion of Pakistan. As parties to the partition process, both countries had agreed that the rulers of princely states would be given the right to opt for either Pakistan or India or—in special cases—to remain independent. Kashmir's population was overall 77 per cent Muslim but with internal areas of non-Muslim majority. It shared a boundary with both India and Pakistan. Pakistan anticipated that the Maharaja would accede to Pakistan, when the British paramountcy ended on 14–15 August. When he hesitated to do this, Pakistan launched a guerrilla infiltration of Pashtun tribals meant to frighten its ruler into submission.[29] Instead the Maharaja appealed to Mountbatten[30] for assistance, and the Governor-General agreed on the condition that the ruler accede to India."[31] Once the Maharaja signed the Instrument of Accession, "Indian soldiers entered Kashmir and drove the Pakistani-sponsored irregulars from all but a small section of the state. The United Nations was then invited to mediate the quarrel. The UN mission insisted that the opinion of Kashmiris must be ascertained, while India insisted that no referendum could occur until all of the state had been cleared of irregulars."[31]
In the last days of 1948, a ceasefire was agreed under UN auspices; however, since the plebiscite demanded by the UN was never conducted, relations between India and Pakistan soured,[31] and eventually led to two more wars over Kashmir in 1965 and 1999. India has control of about half the area of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir; Pakistan controls a third of the region, the Northern Areas and Azad Kashmir. According to Encyclopaedia Britannica, "Although there was a clear Muslim majority in Kashmir before the 1947 partition and its economic, cultural, and geographic contiguity with the Muslim-majority area of the Punjab (in Pakistan) could be convincingly demonstrated, the political developments during and after the partition resulted in a division of the region. Pakistan was left with territory that, although basically Muslim in character, was thinly populated, relatively inaccessible, and economically underdeveloped. The largest Muslim group, situated in the Valey of Kashmir and estimated to number more than half the population of the entire region, lay in Indian-administered territory, with its former outlets via the Jhelum valley route blocked."[32]


The UN Security Council on 20 January 1948 passed Resolution 39, establishing a special commission to investigate the conflict. Pursuant to the commission's recommendation, the Security Council ordered in its Resolution 47, passed on 21 April 1948, that the invading Pakistani army retreat from Jammu & Kashmir and that the accession of Kashmir to either India or Pakistan be determined in accordance with a plebiscite to be supervised by the UN. With Pakistan not forgoing its occupation from what it later termed as Azad Kashmir, none of the resolutions of UNSC could come to force.
Post-1948 developments
The eastern region of the erstwhile princely state of Kashmir has also been beset with a boundary dispute. In the late 19th- and early 20th centuries, although some boundary agreements were signed between Great Britain, Afghanistan and Russia over the northern borders of Kashmir, China never accepted these agreements, and the official Chinese position did not change with the communist takeover in 1949. By the mid-1950s the Chinese army had entered the north-east portion of Ladakh.[32]
- "By 1956–57 they had completed a military road through the Aksai Chin area to provide better communication between Xinjiang and western Tibet. India's belated discovery of this road led to border clashes between the two countries that culminated in the Sino-Indian war of October 1962."[32]
China has occupied Aksai Chin since the early 1950s and, in addition, an adjoining region almost 8% of the territory, the Trans-Karakoram Tract was ceded by Pakistan to China in 1963.
Meanwhile, elections were held in Indian Jammu & Kashmir, which brought up the popular Muslim leader Sheikh Abdullah, who with his party National Conference, by and large supported India. The elected Constituent Assembly met for the first time in Srinagar on October 31, 1951.[33] Then The State Constituent Assembly ratified the accession of the State to the Union of India on February 6, 1954 and the President of India subsequently issued the Constitution (Application to J&K) Order under Article 370 of the Indian Constitution extending the Union Constitution to the State with some exceptions and modifications. The State’s own Constitution came into force on January 26, 1957 under which the elections to the State Legislative Assembly were held for the first time on the basis of adult franchise the same year. This Constitution further reiterated the ratification of the State’s accession to Union of India.[33] However, these tidings were not recognized by Pakistan, which has continued to press for a plebiscite to ascertain the wishes of the people. Pakistan set up its own Kashmir, called Azad Kashmir in a tiny Western chunk that it controls. The much larger region of Pakistani Kashmir in the North-West, which was a province named Northern Areas in the erstwhile state, by and large bore no mention in Pakistani laws and Constitution as being of any status, until in 1982 the Pakistani President General Zia ul Haq proclaimed that the people of the Northern Areas were Pakistanis and had nothing to do with the State of Jammu and Kashmir.[34] In 2009, the Pakistani government renamed the Federally-Administered Northern Areas as Gilgit-Baltistan.
Current status and political divisions
The region is divided among three countries in a territorial dispute: Pakistan controls the northwest portion (Northern Areas and Azad Kashmir), India controls the central and southern portion (Jammu and Kashmir) and Ladakh, and China controls the northeastern portion (Aksai Chin and the Trans-Karakoram Tract). India controls the majority of the Siachen Glacier area including the Saltoro Ridge passes, whereas Pakistan controls the lower territory just southwest of the Saltoro Ridge. India controls 101,338 km2 (39,127 sq mi) of the disputed territory, Pakistan 85,846 km2 (33,145 sq mi) and China, the remaining 37,555 km2 (14,500 sq mi).
Jammu and Azad Kashmir lie outside Pir Panjal range, and are under Indian and Pakistani control respectively. These are populous regions. The main cities are Mirpur, Dadayal, Kotli, Bhimber Jammu, Muzaffarabad and Rawalakot.
The Gilgit-Baltistan, formerly called Northern Areas, are a group of territories in the extreme north, bordered by the Karakoram, the western Himalayas, the Pamir, and the Hindu Kush ranges. With its administrative center at the town of Gilgit, the Northern Areas cover an area of 72,971 km² (28,174 mi²) and have an estimated population approaching 1,000,000. The other main city is Skardu.
Ladakh is a region in the east, between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south.[36] Main cities are Leh and Kargil. It is under Indian administration and is part of the state of Jammu and Kashmir. It is one of the most sparsely populated regions in the area and is mainly inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent.[36]
Aksai Chin is a vast high-altitude desert of salt that reaches altitudes up to 5,000 metres (16,000 ft). Geographically part of the Tibetan Plateau, Aksai Chin is referred to as the Soda Plain. The region is almost uninhabited, and has no permanent settlements.
Though these regions are in practice administered by their respective claimants, neither India nor Pakistan has formally recognised the accession of the areas claimed by the other. India claims those areas, including the area "ceded" to China by Pakistan in the Trans-Karakoram Tract in 1963, are a part of its territory, while Pakistan claims the entire region excluding Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract. The two countries have fought several declared wars over the territory. The Indo-Pakistani War of 1947 established the rough boundaries of today, with Pakistan holding roughly one-third of Kashmir, and India one-half, with a dividing line of control established by the United Nations. The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 resulted in a stalemate and a UN-negotiated ceasefire.
Kashmir valley

The Kashmir valley or Vale of Kashmir is a valley between Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. It is around 135 km long and 32 km wide, formed by the Jhelum River.[35] It was called as "Paradise on Earth" by Jahangir. Currently it has population of around 4 million, 97% of whom are Muslim.
It lies completely within Indian administration in the state of Jammu and Kashmir. Srinagar is its main city and also the summer capital of the state. Other main cities are Anantnag and Baramulla. There has been armed insurgency since 1989 due to the conflict. It has access to the rest of India through Banihal Tunnel near Qazigund on NH 1A to Jammu, which is interrupted by snowfall in winter. The popular tourist places in the valley are Gulmarg, Dal Lake, Pahalgam, Amarnath temple etc.
Demographics
In the 1901 Census of the British Indian Empire, Muslims constituted 74.16% of the total population of the princely state of Kashmir and Jammu, Hindus, 23.72%, and Buddhists, 1.21%. The Hindus were found mainly in Jammu, where they constituted a little less than 70% of the population.[37] In the Kashmir Valley, Muslims constituted 95.6% of the population and Hindus 3.24%.[37] These percentages have remained fairly stable for the last 100 years.[38] Forty years later, in the 1941 Census of British India, Muslims accounted for 93.6% of the population of the Kashmir Valley and the Hindus for 4%.[38] In 2003, the percentage of Muslims in the Kashmir Valley was 95%[39] and those of Hindus 4%; the same year, in Jammu, the percentage of Hindus was 66% and those of Muslims 30%.[39] In the 1901 Census of the British Indian Empire, the population of the princely state of Kashmir and Jammu was 2,905,578. Of these 2,154,695 were Muslims (74.16%), 689,073 Hindus (23.72%), 25,828 Sikhs, and 35,047 Buddhists.

Among the Muslims of the princely state, four divisions were recorded: "Shaikhs, Saiyids, Mughals, and Pathans. The Shaikhs, who are by far the most numerous, are the descendants of Hindus, but have retained none of the caste rules of their forefathers. They have clan names known as krams ..."[37] It was recorded that these kram names included "Tantre," "Shaikh,", "Bhat", "Mantu," "Ganai," "Dar," "Damar," "Lon" etc. The Saiyids, it was recorded "could be divided into those who follow the profession of religion and those who have taken to agriculture and other pursuits. Their kram name is "Mir." While a Saiyid retains his saintly profession Mir is a prefix; if he has taken to agriculture, Mir is an affix to his name."[37] The Mughals who were not numerous were recorded to have kram names like "Mir" (a corruption of "Mirza"), "Beg," "Bandi," "Bach," and "Ashaye." Finally, it was recorded that the Pathans "who are more numerous than the Mughals, ... are found chiefly in the south-west of the valley, where Pathan colonies have from time to time been founded. The most interesting of these colonies is that of Kuki-Khel Afridis at Dranghaihama, who retain all the old customs and speak Pashtu."[37] Among the main tribes of Muslims in the princely state are the Butts, Dar, Lone, Jat, Gujjar, Rajput, Sudhan and Khatri. A small number of Butts, Dar and Lone use the title Khawaja and the Khatri use the title Shaikh the Jats may often use the title of Chaudhary. All these tribes are indigenous of the princely state and many Hindus also belong to these tribes.
The Hindus were found mainly in Jammu, where they constituted a little less than 60% of the population.[37] In the Kashmir Valley, the Hindus represented "524 in every 10,000 of the population (i.e. 5.24%), and in the frontier wazarats of Ladhakh and Gilgit only 94 out of every 10,000 persons (0.94%)."[37] In the same Census of 1901, in the Kashmir Valley, the total population was recorded to be 1,157,394, of which the Muslim population was 1,083,766, or 93.6% and the Hindu population 60,641.[37] Among the Hindus of Jammu province, who numbered 626,177 (or 90.87% of the Hindu population of the princely state), the most important castes recorded in the census were "Brahmans (186,000), the Rajputs (167,000), the Khattris (48,000) and the Thakkars (93,000)."[37]
In the 1911 Census of the British Indian Empire, the total population of Kashmir and Jammu had increased to 3,158,126. Of these, 2,398,320 (75.94%) were Muslims, 696,830 (22.06%) Hindus, 31,658 (1%) Sikhs, and 36,512 (1.16%) Buddhists. In the last census of British India in 1941, the total population of Kashmir and Jammu (which as a result of the second world war, was estimated from the 1931 census) was 3,945,000. Of these, the total Muslim population was 2,997,000 (75.97%), the Hindu population was 808,000 (20.48%), and the Sikh 55,000 (1.39%).[40]
According to political scientist Alexander Evans, 1,00,000 of the total population of 7,00,000 of Kashmir Hindus or Brahmins, also called Kashmiri Pandits since Kashmiri Hindus has no caste system as Vedic Arya Hindus (Kashmir described as Aryan homeland by many famous scholars[41]), left the state of Jammu and Kashmir 300,000 of whom, half all internally displaced, are in UN refugee camps of Jammu & Udhampur [42]
| Administered by | Area | Population | % Muslim | % Hindu | % Buddhist | % Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| India | Kashmir Valley | ~4 million | 95% | 4%* | – | – |
| Jammu | ~3 million | 30% | 66% | – | 4% | |
| Ladakh | ~0.25 million | 50% | – | 46% | 3% | |
| Pakistan | Azad Kashmir | ~2.6 million | 100% | – | – | – |
| Northern Areas | ~1 million | 99% | – | – | – | |
| China | Aksai Chin | – | – | – | – | – |
Culture and cuisine

Kashmiri cuisine includes dum aloo (boiled potatoes with heavy amounts of spice), tzaman (a solid cottage cheese), rogan josh (lamb cooked in heavy spices), yakhiyn (lamb cooked in curd with mild spices), hakh (a spinach-like leaf), rista-gushtaba (minced meat balls in tomato and curd curry),danival korme and of course the signature rice which is particular to Asian cultures. The traditional wazwan feast involves cooking meat or vegetables, usually mutton, in several different ways.
Alcohol is strictly prohibited in most places. There are two styles of making tea in the region: nun chai, or salt tea, which is pink in colour (known as chinen posh rang or peach flower colour) and popular with locals; and kahwah, a tea for festive occasions, made with saffron and spices (cardamom, cinamon,sugar, noon chai leaves), and lipton tea.
Economy
Kashmir's economy is centred around agriculture. Traditionally the staple crop of the valley was rice, which formed the chief food of the people. In addition, Indian corn, wheat, barley and oats were also grown. Given its temperate climate, it is suited for crops like asparagus, artichoke, seakale, broad beans, scarletrunners, beetroot, cauliflower and cabbage. Fruit trees are common in the valley, and the cultivated orchards yield pears, apples, peaches, and cherries. The chief trees are deodar, firs and pines, chenar or plane, maple, birch and walnut, apple, cherry.
Historically, Kashmir became known worldwide when Cashmere wool was exported to other regions and nations (exports have ceased due to decreased abundance of the cashmere goat and increased competition from China). Kashmiris are well adept at knitting and making Pashmina shawls, silk carpets, rugs, kurtas, and pottery. Saffron, too, is grown in Kashmir. Efforts are on to export the naturally grown fruits and vegetables as organic foods mainly to the Middle East. Srinagar is known for its silver-work, papier mache, wood-carving, and the weaving of silk.
The economy was badly damaged by the 2005 Kashmir earthquake which, as of October 8, 2005, resulted in over 70,000 deaths in the Pakistan-controlled part of Kashmir and around 1,500 deaths in Indian controlled Kashmir.
The Indian-administered portion of Kashmir is believed to have potentially rich rocks containing hydrocarbon reserves.[43][44]
History of Tourism in Kashmir
During the 19th century rule, Kashmir was a popular tourist destination due to its climate. Only 200 passes a year were issued by the government. European sportsmen and travellers, in addition to residents of India, traveled there freely. The railway to Rawalpindi, and a road thence to Srinagar made access to the valley easier. When the temperature in Srinagar rose at the beginning of June, the residents migrated to Gulmarg, which was a fashionable hill station during British rule. This great influx of visitors resulted in a corresponding diminution of game for the sportsmen. Special game preservation rules were introduced, and nullahs were let out for stated periods with a restriction on the number of head to be shot. Rawalakot was another popular destination.
See also
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 47
- Line of Control
- Kashmir Conflict
- Who's Who of Kashmir
- Kargil War
- 2005 Kashmir earthquake
- List of Jammu and Kashmir related articles
- Srinagar
References
- ↑ http://www.un.org/Depts/dpko/missions/unmogip/
- ↑ MBH 7.4.5.
- ↑ MBH 7/91/39-40.
- ↑ Mahabharata 7.4.5
- ↑ Political History of Ancient India, from the Accession of Parikshit to the ..., 1953, p 150, Dr H. C Raychaudhuri - India; Ethnic Settlements in Ancient India: (a Study on the Puranic Lists of the ..., 1955, p 78, Dr S. B. Chaudhuri; An Analytical Study of Four Nikāyas, 1971, p 311, D. K.Barua - Tipiṭaka.
- ↑ Basham, A. L. (2005) The wonder that was India, Picador. Pp. 572. ISBN 033043909X, p. 110.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Imperial Gazetteer of India, volume 15. 1908. Oxford University Press, Oxford and London. pp. 93-95.
- ↑ "Kaashmir." The Oxford English Dictionary. 2nd ed. 1989.
- ↑ A.K. Warder, Indian Buddhism. Motilal Banarsidass 2000, page 256.
- ↑ A.K. Warder, Indian Buddhism. Motilal Banarsidass 2000, pages 263-264.
- ↑ Tapasyananda, Swami (2002). Sankara-Dig-Vijaya. pp. 186–195.
- ↑ Triadic Heart of Shiva, Paul E. Muller-Ortega, page 12
- ↑ Introduction to the Tantrāloka, Navjivan Rastogi, page 27
- ↑ Key to the Vedas, Nathalia Mikhailova, page 169
- ↑ The Pratyabhijñā Philosophy, Ganesh Vasudeo Tagare, page 12
- ↑ Companion to Tantra, S.C. Banerji, page 89
- ↑ Doctrine of Divine Recognition, K. C. Pandey, page V
- ↑ Introduction to the Tantrāloka, Navjivan Rastogi, page 35
- ↑ Luce dei Tantra, Tantrāloka, Abhinavagupta, Raniero Gnoli, page LXXVII
- ↑ http://www.historyofjihad.org/india.html
- ↑ http://www.islam-watch.org/AliSina/from_rags_to_riches.htm
- ↑ 'Over time, however, the Sufiana governance gave way to outright Muslim monarchs' appears in the article which is true but no explanation for it is given which I provided. The reason is Islamic requirement to turn the world into Darul Islam as per Koran and hence link of the 'Holy' Quran with the appropriate verses was quoted as reference (just click the verses in link to see them in Koranic perspective). Another was a site on the History of Jihad in India with special reference to Kashmir which by any standards are most reliable sources and none can ignore Quranic instructions as non-reliable sources while discussing on Islam & its nature, in this case Islamic Government. Likewise without history of jihad the article is incomplete not only in elucidating the quoted line at the top but also in writing about overall Muslim rule in Kashmir!
- ↑ Muhammad Qãsim Hindû Shãh Firishta : Tãrîkh-i-Firishta, translated by John Briggs under the title "History of the Rise of the Mahomedan Power in India." First published in 1829, New Delhi Reprint 1981.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 Imperial Gazetteer of India, volume 15. 1908. "Kashmir: History." pp. 94-95.
- ↑ Treaty of Amritsar, March 16, 1846.
- ↑ From the text of the Treaty of Amritsar, signed March 16, 1846.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Bowers, Paul. 2004. "Kashmir." Research Paper 4/28, International Affairs and Defence, House of Commons Library, United Kingdom.
- ↑ "INDIA-PAKISTAN: Death in the Vale". Time. 1947-11-10. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,793895,00.html.
- ↑ Viscount Louis Mountbatten, the last Viceroy of British India, stayed on in independent India from 1947 to 1948, serving as the first Governor-General of the Union of India.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 Stein, Burton. 1998. A History of India. Oxford University Press. 432 pages. ISBN 0195654463. Page 368.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 Kashmir. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved March 27, 2007, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 "Major Events". Jammu and Kashmir Government, India. http://jammukashmir.nic.in/profile/majev.htm#1. Retrieved 2007-01-09.
- ↑ "A Comprehensive Note on Jammu & Kashmir: The Northern Areas". Embassy of India, Washington D.C.. http://www.indianembassy.org/policy/Kashmir/Kashmir_MEA/Northern_Areas.html. Retrieved 2007-01-09.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/312921/Vale-of-Kashmir
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 Jina, Prem Singh (1996). Ladakh: The Land and the People. Indus Publishing. ISBN 8173870578.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 37.2 37.3 37.4 37.5 37.6 37.7 37.8 Imperial Gazetteer of India, volume 15. 1908. Oxford University Press, Oxford and London. pp. 99-102.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Rai, Mridu. 2004. Hindu Ruler, Muslim Subjects: Islam and the History of Kashmir. Princeton University Press. 320 pages. ISBN 0691116881. p. 37.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 BBC. 2003. The Future of Kashmir? In Depth.
- ↑ Brush, J. E. 1949. "The Distribution of Religious Communities in India" Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 39(2):81-98.
- ↑ http://books.google.co.in/books?id=8VnAk14pODsC&pg=PA219&lpg=PA219&dq=kashmir+is+aryan+homeland&source=bl&ots=AHbcaP7ixW&sig=TFzyL0AClsBU8WjEokR-N1yk9Uw&hl=en&ei=lXAGTLPrFYK7rAeFrqjnDA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=10&ved=0CEQQ6AEwCQ
- ↑ CIA Factbook: India–Transnational Issues
- ↑ Iftikhar Gilani (2008-10-22). "Italian company to pursue oil exploration in Kashmir". Daily Times. http://www.dailytimes.com.pk/default.asp?page=2008\10\22\story_22-10-2008_pg7_41. Retrieved 2009-11-20.
- ↑ Ishfaq-ul-Hassan (2008-02-22). "India, Pakistan to explore oil jointly". Daily News and Analysis. http://www.dnaindia.com/india/report_india-pakistan-to-explore-oil-jointly_1152227. Retrieved 2009-11-20.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (Eleventh ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (Eleventh ed.). Cambridge University Press.
KASHMIR LIT e JOURNAL http://kashmirlit.org/default.aspx Article on Kashmir http://www.imow.org/community/directory/user/index?id=19180 scroll down for kashmir project) http://hrc.berkeley.edu/past_fellows.html Article on World Pulse http://www.worldpulse.com/magazine/articles/my-life-my-kashmir
Further reading
- Blank, Jonah. "Kashmir–Fundamentalism Takes Root," Foreign Affairs, 78,6 (November/December 1999): 36-42.
- Drew, Federic. 1877. “The Northern Barrier of India: a popular account of the Jammoo and Kashmir Territories with Illustrations; 1st edition: Edward Stanford, London. Reprint: Light & Life Publishers, Jammu. 1971.
- Evans, Alexander. Why Peace Won’t Come to Kashmir, Current History (Vol 100, No 645) April 2001 p. 170-175.
- Hussain, Ijaz. 1998. "Kashmir Dispute: An International Law Perspective", National Institute of Pakistan Studies.
- Irfani, Suroosh, ed "Fifty Years of the Kashmir Dispute": Based on the proceedings of the International Seminar held at Muzaffarabad, Azad Jammu and Kashmir August 24–25, 1997: University of Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Muzaffarabad, AJK, 1997.
- Joshi, Manoj Lost Rebellion: Kashmir in the Nineties (Penguin, New Delhi, 1999).
- Khan, L. Ali The Kashmir Dispute: A Plan for Regional Cooperation 31 Columbia Journal of Transnational Law, 31, p. 495 (1994).
- Knight, E. F. 1893. Where Three Empires Meet: A Narrative of Recent Travel in: Kashmir, Western Tibet, Gilgit, and the adjoining countries. Longmans, Green, and Co., London. Reprint: Ch'eng Wen Publishing Company, Taipei. 1971.
- Köchler, Hans. The Kashmir Problem between Law and Realpolitik. Reflections on a Negotiated Settlement. Keynote speech delivered at the "Global Discourse on Kashmir 2008." European Parliament, Brussels, 1 April 2008.
- Lamb, Hertingfordbury, UK: Roxford Books,1994, "Kashmir: A Disputed Legacy.
- Moorcroft, William and Trebeck, George. 1841. Travels in the Himalayan Provinces of Hindustan and the Panjab; in Ladakh and Kashmir, in Peshawar, Kabul, Kunduz, and Bokhara... from 1819 to 1825, Vol. II. Reprint: New Delhi, Sagar Publications, 1971.
- Neve, Arthur. (Date unknown). The Tourist's Guide to Kashmir, Ladakh, Skardo &c. 18th Edition. Civil and Military Gazette, Ltd., Lahore. (The date of this edition is unknown - but the 16th edition was published in 1938).
- Schofield, Victoria. 1996. Kashmir in the Crossfire. London: I B Tauris.
- Stein, M. Aurel. 1900. Kalhaṇa's Rājataraṅgiṇī–A Chronicle of the Kings of Kaśmīr, 2 vols. London, A. Constable & Co. Ltd. 1900. Reprint, Delhi, Motilal Banarsidass, 1979.
- Younghusband, Francis and Molyneux, Edward 1917. Kashmir. A. & C. Black, London.
- Norelli-Bachelet, Patrizia. "Kashmir and the Convergence of Time, Space and Destiny", 2004; ISBN 0-945747-00-4. First published as a four-part series, March 2002 - April 2003, in 'Prakash', a review of the Jagat Guru Bhagavaan Gopinath Ji Charitable Foundation. [1]
- Muhammad Ayub. An Army; Ita Role & Rule (A History of the Pakistan Army from Independence to Kargil 1947-1999) Rosedog Books, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania USA 2005. ISBN 0-8059-9594-3.
External links
- Instrument of Accession
- United Nations Military Observers Group in Kashmir
- Official website of the Jammu and Kashmir Government (Indian-administered Kashmir)
- Official website of the Azad Jammu and Kashmir Government (Pakistan-administered Kashmir)
- Letter of Baroness Nicholson which refers to the 1909 map of Kashmir
- Excerpts of telegram dated 26 October 1947 from Jawaharlal Nehru to the British Prime Minister, Clement Attlee
- Kashmir Website with Historical Timeline
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Territory | Currently Administered by | Claimants |
| Land: | Aksai Chin | ||
| Baekdu Mountain | |||
| Heixiazi / Bolshoy Ussuriysky (Eastern part)2 | |||
| Indo-Bangladesh enclaves3 | |||
| Kachin State | |||
| Kashmir3 | |||
| Kayin State | |||
| Korean Peninsula and its adjacent islands3 | |||
| Mainland China | |||
| North Borneo (Sabah)2 | |||
| Outer Mongolia2 | |||
| Pamir Mountains3 | |||
| Patani | |||
| Shan State | |||
| Sixty-Four Villages East of the River2 | |||
| South Tibet (now Arunachal Pradesh of India) | |||
| Tannu Uriankhai (now Tuva Republic of Russia)2 | |||
| Trans-Karakoram Tract | |||
| Wa State | |||
| Islands and Waters: | Diaoyutai / Senkaku Islands | ||
| Kinmen | |||
| Kori Creek2 | |||
| Liancourt Rocks | |||
| Macclesfield Bank | |||
| Matsu | |||
| Paracel Islands | |||
| Pedra Branca, Middle Rocks, and South Ledge | |||
| Pratas Islands | |||
| Scarborough Shoal | |||
| Socotra Rock | |||
| Southern Kuril Islands | |||
| Spratly Islands3 | |||
| Taiwan and Penghu2 | |||
| Notes: | 1Government in exile/exiled group. 2Inactive dispute. 3Divided among multiple claimants. |
||


